Back and Joint Pain
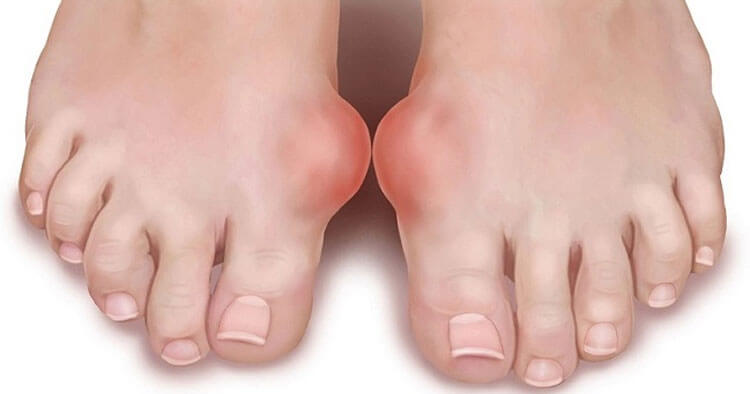
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Gouty Arthritis
How is Gouty Arthritis Diagnosed?
If the attack is the first of its kind then the doctor will look for elevated urate levels in the blood (with gouty arthritis these are often elevated, but not always). They may even take a sample of fluid from the joint in order to make a definite diagnosis. If the attack is related to gout, then uric acid crystals can be visualized under a microscope.
Other investigations and signs useful in the diagnosis of gout can include:
- X-ray: However this may not reveal much until late in the disease process.
- The use of Dual-energy CT (DECT) is a relatively new imaging technique in the treatment of gouty arthritis with a high sensitivity and specificity for the detection of gouty tophi. The imaging is useful for the detection of deposits in areas that are difficult to assess clinically as well as any morphological changes of gout such as erosions and joint destruction. It is also useful in the assessment of the conditions response to treatment through the use of before and after comparison imaging following the application of a treatment course.
- Urea and electrolytes: Signs of renal impairment.
What Is The Prognosis of Gouty Arthritis?
The classical clinical presentation of gout is that of an acutely painful, inflamed joint (which is often the big toe) which resolves within a week. Chronic gout involving many joints (polyarticular) is less common. This form of gout has a worse prognosis as it leads to gradual joint destruction and loss of function.
Due to that attacks of gouty arthritis can cause damage to the affected joint and nearby bone it is advisable people should seek medical help when suffering an “attack” of gout. Prompt treatment can help significantly in relieving the pain and inflammation of acute gouty arthritis.
Treating Gout
A good starting point is visiting your doctor and they may refer you to a rheumatologist if necessary. Acute attacks of gouty arthritis are generally treated with high doses of oral NSAIDs and corticosteroid injections locally into the affected area are sometimes used.
Without treatment an attack of gout will usually resolve within one or two weeks. With treatment and medication, the attack can be resolved within several days (however, the crystals still remain in the joint).
Long term management of gout following the settling of an acute attack is focused at lifestyle factors:
- Weight management, maintaining a healthy body weight.
- Reduced alcohol consumption and avoiding binge drinking.
- Staying hydrated, drinking plenty of water.
- Avoidance of purine rich foods such as offal, oily fish, excess protein…
- Stopping the use of diuretics.
- Prescription of drugs to reduce serum uric acid levels.
Early diagnosis and treatment with gouty arthritis is important. The primary goal in the long term management is reducing the level of uric acid in the blood (so it cannot form crystals in the tissues or joints causing joint damage). With healthy lifestyle choices coupled with an appropriate treatment regime as advised by your doctor gout is generally successfully managed.
Disclaimer: Sydney Physio Clinic provides this information as an educational service and is not intended to serve as medical advice. Anyone seeking specific advice or assistance on Diagnosis And Treatment Of Gouty Arthritis should consult his or her physiotherapist, general practitioner or otherwise appropriately skilled practitioner.